
The sound frequency doubles for corresponding notes from one octave to the next. Notably, an equal-tempered octave has twelve half steps (semitones) spaced equally in terms of the sound frequency ratio. Whole steps and half steps are explained mathematically in a related article, Twelfth root of two. Where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line in the figure). Whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: The intervals from the tonic (keynote) in an upward direction to the second, to the third, to the sixth, and to the seventh scale degrees of a major scale are called major. Structure The pattern of whole and half steps characteristic of a major scale In Hindustani classical music, it is known as Bilaval. In Carnatic music, it is known as Sankarabharanam.
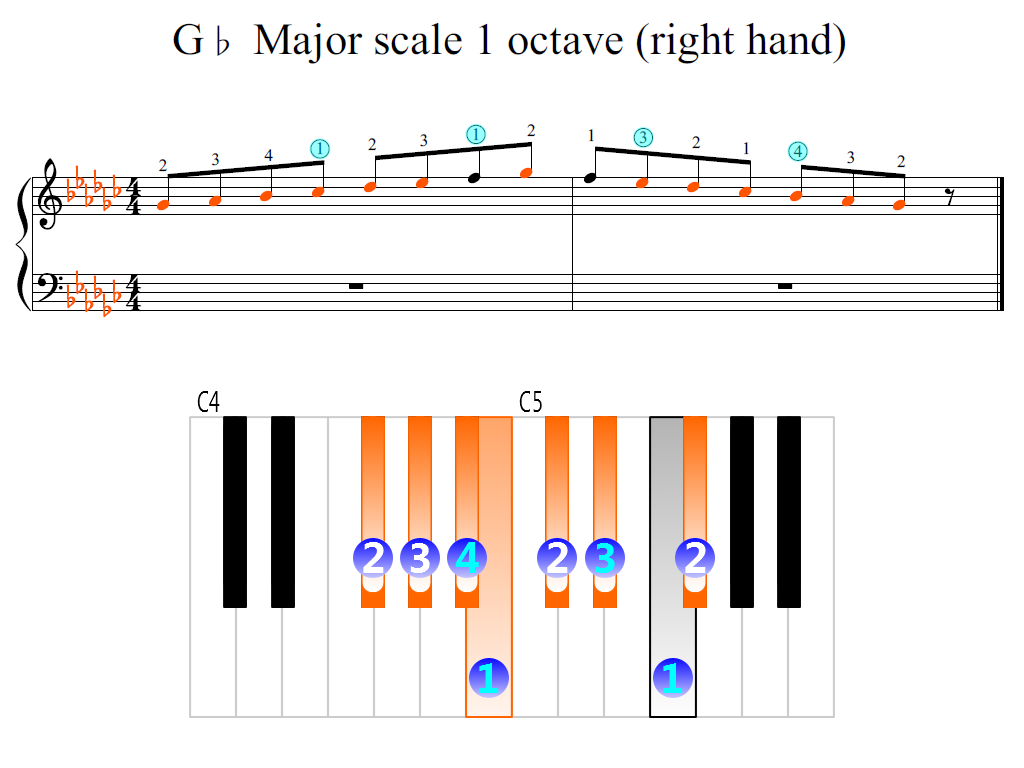

The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music.

Audio playback is not supported in your browser.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
